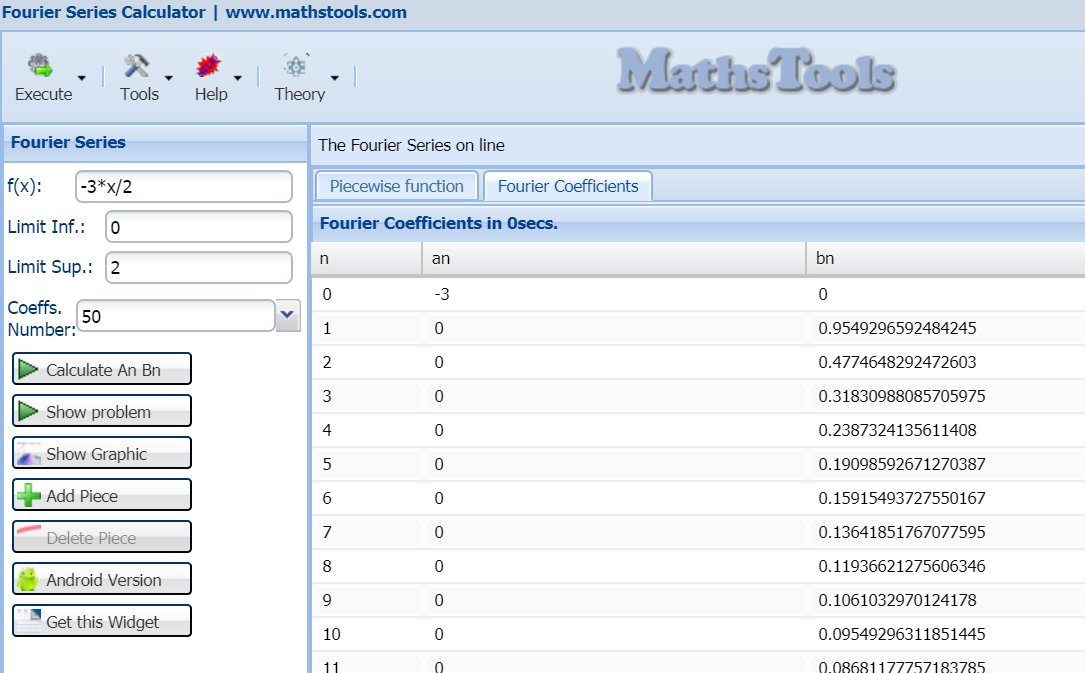
On-Line Fourier Series Calculator is an interactive app for Fourier Series Coefficients
Calculations (Up to 10000 elements) for user-defined piecewise functions up to 5 pieces, for example:
\( f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} 0 & x \in [-1,0)\\ x+1 & x \in [0,1] \end{matrix}\right. \)
Produces the result:
Note that function have to be within integrable-functions space or L
1 on selected Interval as we shown at theory sections.
FourierSeries Calculator calculates Fourier Coefficients, analytic and numeric integrals
and it is usefull to plot 1-variable functions and its Fourier series on a generic user-defined interval.
Click here to access to Fourier Series Calculator
Calculations accuracy depends largely on size-interval and the number of selected coefficients.
Use it is as follows:
1) Write the lower end of the range in the text box labeled Limit inf.
2) Enter the upper range in the text box labeled Limit Sup.
3) Write the function in the text box with the label function
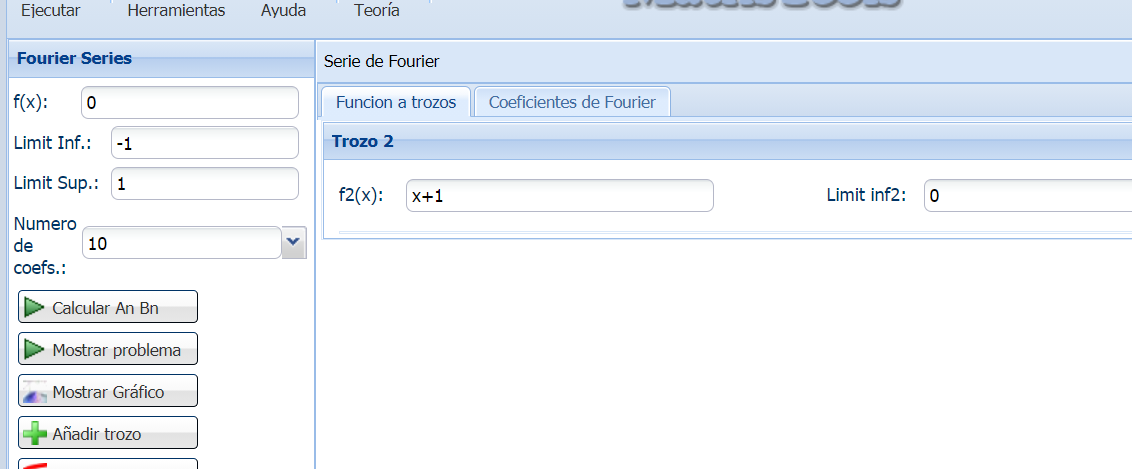
In the piecewise function case, operate as follows:
1) Write the lower end of the range in the text box labeled Limit inf.
2) Enter the upper range in the text box labeled Limit Sup.
3) Write the first function in the text box with the label function
.
4) Enter the upper sub-range in the text box labeled Subinterval 1.
5) Write the function as defined in the first sub-interval in the text box labeled subinterval 1
.
For instance let's suppose we have following piecewise function:
\( f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} 0 & x \in [-1,0)\\ x+1 & x \in [0,1] \end{matrix}\right. \)
Then the fields should be filled as
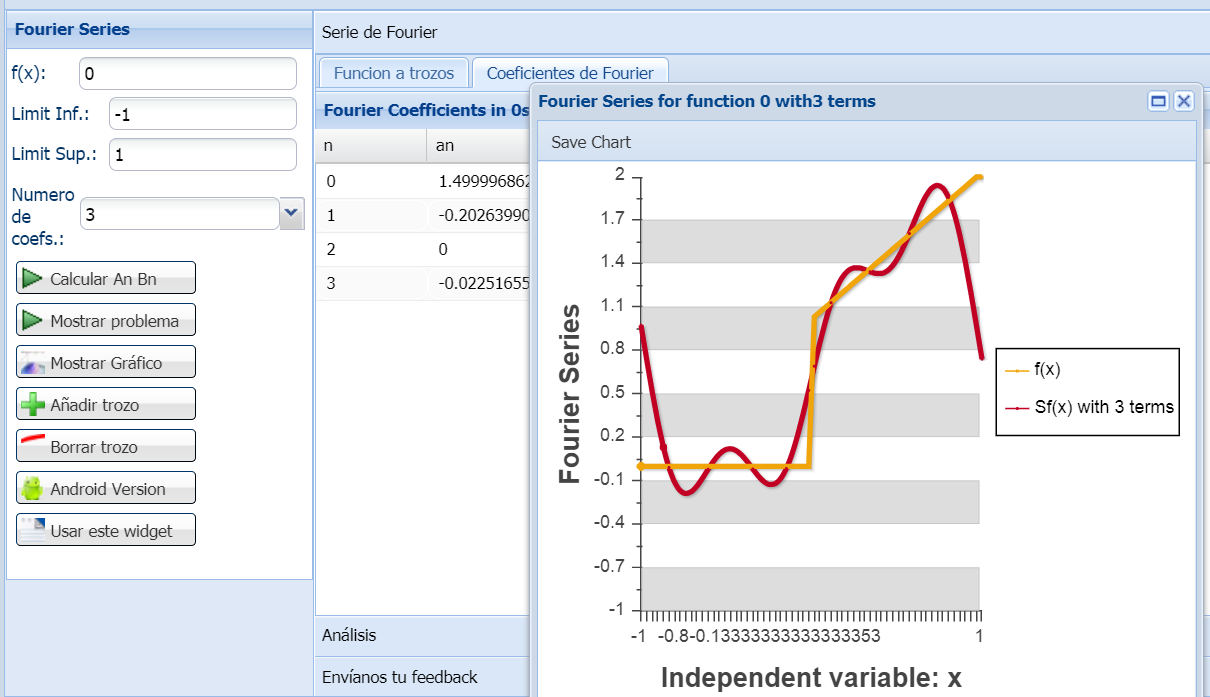
After the A
n, B
n calculations, it is possible to plot the function and its Fourier Series by clicking "Show Graph". In this case
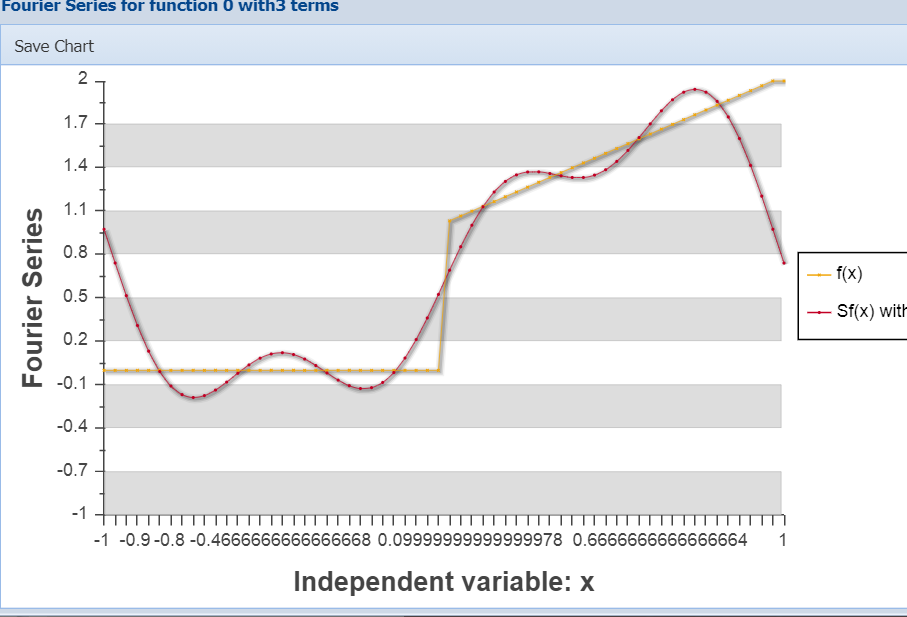
By default, the problem starts with a picewise-continuous function given in following interval:
\( f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} x^2+x+1 & x \in [-1,0)\\ 0 & x \in [0,1] \end{matrix}\right. \)
How it works?
To calculate Fourier coefficients we apply numerical integration methods seen in the
numerical methods section. Wtih them we can approximate the integrals given by the Fourier Series formulae:
$$ f(x)=\frac{A_{0}}{2} + \sum_{n=1}^{\infty}(A_n cos nx + B_nsin nx ) $$
Where
\( A_i, B_i \in \mathbb{R} \)
and
\( A_0= \frac{1}{\pi} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) dx\)
\( A_n= \frac{1}{\pi} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) cos nx dx\)
\( B_n= \frac{1}{\pi} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi}f(x) sin nx dx\)
In Fourier coefficients case, there are several methods to make the calculations programmed here by the owners of
Mathstools .
To calculate the derivative of the function: uses severeal numerical methods to derivate.
To calculate the primitive function: numerical integration methods seen in the
numerical methods section are applied.
Note that in numerical analysis, errors are obtained due to the particular methods and the limitation of arithmetic computer as well.
In the Fourier coefficients calculations case, it depends on the function and size of the chosen integration interval. In default problem
the error in calculating the Fourier coefficients is O (1e-8). For the numerical integration is O (1e-11) and in the derivative it is O (1e-14).
Click here to access to Fourier Series Calculator