Maximize (x + 3y)
Subject to
x + y ≤ 3
x + y ≤ 2
x - y ≥ 1
x, y ≥ 0
Subject to
x + y ≤ 3
x + y ≤ 2
x - y ≥ 1
x, y ≥ 0
The feasible region is bounded and nonempty. Thus if the ploblem has optimal solution, it will be finite.
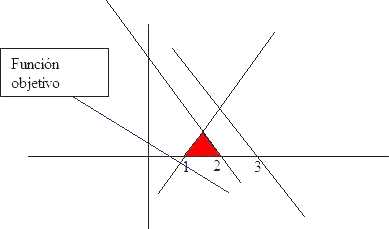
In addition the objective function grows in the direction of growth of x and y coordinates, the problem has finite optimal solution into of the extreme points of feasible region.
Clearily, even at simple view is visible that the maximum is reached at point (3 / 2, 1 / 2) with optimal value for objective function 3.


